BILATERAL OCULAR ISCHEMIC SYNDROME
Abstract
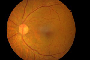
Ocular ischemic syndrome is a rare condition, which is caused by ocular hypoperfusion due to stenosis or occlusion of the common carotid or internal carotid arteries. Atherosclerosis is the major cause of changes in the carotid arteries. Here we report a case of bilateral ocular ischemic syndrome in a 51 year old male who presented to us with complaint of defective vision in right eye. On examination patient was having neovascularization of iris in both eyes, neovascularization of the disc in left eye and mature cataract in right eye. Patient was suggested to undergo carotid doppler
and fundus fluorescein angiography. Carotid doppler showed severe carotid artery stenosis on both sides and Fundus Fluorescein Angiography showed features suggestive of ocular ischemic syndrome. Patient underwent panretinal photocoagulation in left eye and is awaiting cataract surgery in right eye followed by repeat Fundus Fluorescein Angiography.
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Hart, CT, Haworth, S. Bilateral common carotid occlusion with hypoxic ocular sequelae. Br J Ophthalmol. 1971;55:383–388
Hoefnagels, KLJ. Rubeosis of the iris associated with occlusions of the carotid artery. Ophthalmologica. 1964;148:196–200
Eggleston, TF, Bohling, CA, Eggleston, HC et al, Photocoagulation for ocular ischemia associated with carotid artery occlusion. Ann Ophthalmol. 1980;12:84–87
Kahn, MK, Green, WR, Knox, DL et al, Ocular features of carotid occlusive disease. Retina. 1986;6:239–252
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities