A case of solitary choroidal tuberculoma in an immunocompetent young male
Abstract
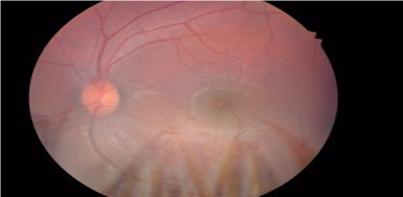
Intraocular tuberculosis is a rare event and occurs in 1 of all diagnosed cases of tuberculosis. It occurs by haematogenous spread of mycobacterial organism. Choroidal tuberculosis is the most common initial manifestation of intraocular tuberculosis. A 19 yr old male presented with complaints of diminished vision in RE for 10 days. Best corrected visual acuity RE 660 LE 66.BE Anterior segment normal. Fundus examination RE shows a solitary yellowish white choroidal lesion with irregular, fuzzy margins involving the macula, along with a superficial pre-retinal hemorrhage and surrounding retinal edema. Disc was mildly hyperemic. FFA confirmed a choroidal lesion with early hypofluorescence and late moderate hyper fluorescence with surrounding blocked fluorescence due to pre-retinal hemorrhage. Mantoux test and Quantiferon TB Gold assay were positive. He was started on four drug regimen ATT. After 2 weeks, oral steroids in tapering doses was started. After 4 weeks, the lesion started to resolve with vision improving to 618.
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Ocular tuberculosis. A prospective study in a general hospital. Medicine (Baltimore) 1997, 76:53–61. Bouza E, Merino P, Munoz P, et al.
Biswas J, Badrinath SS. Ocular morbidity in patients with active systemic tuberculosis. Int Ophthalmol 1995- 1996;19:293-8.
Illingworth RS, Lorber J. Tubercles of the choroid. Arch Dis Child 1956;31:467-9.
Mehta S. Healing patterns of choroidal tubercles after antitubercular therapy: a photographic and OCT study. J.Ophthalmic Inflamm. Infect. 2(2), 95–97(2012).
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities