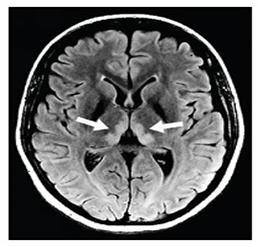
A rare complication of hyperemesis during pregnancy-Wernicke's encephalopathy
Abstract
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Cirignotta F, Manconi M, Mondini S, Buzzi G, Ambrosetto P. Wernicke–Korsakoff encephalopathy and polyneuropathy after gastroplasty for morbid obesity: Report of a case. Arch Neurol. 2000;57:1356–9.
Netravathi M, Sinha S, Taly AB, Bindu PS, Bharath RD. Hyperemesis-gravidarum-induced Wernicke's encephalopathy: Serial clinical, electrophysiological and MR imaging observations. J Neurol Sci.2009;284:214–6.
Harper C. The incidence of Wernicke's encephalopathy in Australia: A neuropathological study of 131 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983;46:593–8.
Wernicke C. Lehrbuch der gehirnkrankheiten furaerzte und studirende. Kassel Theodor Fischer. 1881;2:229-42.
Caine D, Halliday GM, Kril JJ, Harper CG. Operational criteria for the classification of chronic alcoholics: identification of Wernicke’s encephalopathy. JNNP. 1997;62:51-60
Sulaiman W, Othman A, Mohamad M, Salleh HR, Mushahar L. Wernicke›s encephalopathy associated with hyperemesis gravidarum-A case report. Malays J Med Sci. 2002;9:43–6.
Hazell AS, Todd KG, Butterworth RF. Mechanism of neuronal cell death in Wernicke’s ncephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 1998;13:97-122.
Togay-Isikay C, Yigit A, Mutluer N. Wernicke’s encephalopathy due to hyperemesis gravidarum: an under-recognised condition. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2001;41:453-6
Baker H, Frank O, Thomson AD, Langer A, Munves ED, De Angelis B, et al. Vitamin profile of 174 mothers and newborns at parturition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1975;28:59–65.
Galvin R, Brathen G, Ivashynka A, Hillbom M, Tanasescu R, Leone MA. EFNS guidelines for diagnosis, therapy and prevention of Wernicke encephalopathy. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17:1408–18.
Manzanares W, Hardy G. Thiamine supplementation in the critically ill. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011;14:610–7.
Harper C. The incidence of Wernicke’s encephalopathy in Australia: a neuropathological study of 131 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psych, 1983;46: 593–598.
Thomson AD, Marshall EJ. The natural history of Wernicke’s encephalopathy and Korsakoff’s Psychosis. Alcohol Alcohol, 2006;41:151-158.
Day E, Bentham P, Callaghan R, et al. Thiamine for Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome in people at risk from alcohol abuse. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Issue 1, 2009, CD004033.pub2.
Martin RJ (2004). Central pontine and extrapontinemyelinosis:The osmotic demyelination syndromes. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 75 (Suppl III) 22-28 Ropper AH and Brown RH (2005)
MacGibbon KW, Fejzo, MS, Mullin PM (2015). Mortality Secondary to Hyperemesis Gravidarum: A Case Report
Rinsho Shinkeigaku. Clinical Neurology. 1994 Jun;34(6):599-601. Beneficial effect of steroid pulse therapy on Wernicke-korsakoff syndrome due to hyperemesis gravidarum [Article in Japanese] Iwamoto Y, Okuda B, Miyata Y, Tachibana H, Sugita M. Fifth Department of Internal Medicine, Hyogo College of Medicine.
Manzo G, De Gennaro A, Cozzolino A, Serino A, Fenza G, Manto A. MR Imaging Findings in Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Acute Wernicke’s Encephalopathy: A Review. BioMed Res Int. 2014;2014:1-12
Thiamine deficiency and its prevention and control in major emergencies (WHO) http://www.unhcr.org/4cbef0959.pdf
Ortega R, Martínez R, Andrés P, Marín-Arias L, López-Sobaler A. Thiamin status during the third trimester of pregnancy and its influence on thiamin concentrations in transition and mature breast milk. BJN. 2004;92(01):129.
Tanasescu R, Dumitrescu L, Dragos C, Luca D, Oprisan A, Coclitu C, et al. (2012). Wernicke’s Encephalopathy, Miscellanea on Encephalopathies - A Second Look, Dr. Radu Tanasescu (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-51-0558-9, InTech, DOI: 10.5772/27988.
Chiossi G, Neri I, Cavazzuti M, Basso G, Facchinetti F. Hyperemesis gravidarum complicated by Wernicke encephalopathy: background, case report, and review of the literature. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2006;61(4):255- 268.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities