Study of Association of Transrectal Ultrasonogram Derived Parameters with Acute Urinary Retention in Symptomatic Patients with Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy
Abstract
INTROUCTION: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
for decades has been a significant major problem for
elderly men. BPH is associated with bothersome lower
urinary tract symptoms (mild to severe) namely urinary
frequency, urgency, feeling of incomplete bladder
emptying, nocturia, and decreased force of their urinary
stream. Many of the patients suffering from BPH undergo
surgery for having one of the absolute indications for
surgery (refractory urine retention despite adequate and
effective medical treatment, presence of urinary tract
infections, repeated episodes of infections, gross
hematuria with multiple episodes, pathological and/or
physiological changes of the organs directly or indirectly
involved namely secondary to obstruction). However a
large portion of patients undergo surgery for having
a relative indication, namely sever LUTs not responding to
efficient medical therapy. This relative indication is purely
subjective, and although many diagnostic tools are present
to aid in the assessment of such patients (uroflowmetry,
post voiding residual urine and pressure flow studies),
none of them were totally reliable, either for their weak
correlation or their invasiveness. In this study, we tried to
test the transition zone index and other derived parameters
to determine if calculating such a figure would help in the
assessment of prostatic patients. AIM OF THE STUDY:
The aim of this study is to derive and confirm the
association between the transrectal ultra sonogram
derived prostate measures and the development of acute
urinary retention in symptomatic prostatic patients and
trying to evaluate the clinical usefulness of calculating this
index. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Cross sectional
clinical study of Patients attending Urology OPD and in
patients at Kilpauk Medical College Hospital and Govt.
Royapettah Hospital in the age group between 45 and 85
with lower urinary tract symptoms of benign prostatic
hyperplasia. The study period is from June 2016 to March
2017. TRUS based calculation the transition zone (TZ)
volume, the transition zone index (TZ index = TZ volume/total
prostate volume), the total prostate volume, and presumed
circle area ratio (PCAR). The study of association between
these parameters and acute urinary retention was done using
statistical analysis software. RESULTS: The maximum
number of patients with urinary retention is found in the group
with duration of symptoms of 4-6 yrs (32.10%), followed by
the group with duration between 6-8 yrs. In the frequency
distribution for total prostate volume, acute retention of urine
was found to be maximum (43%) in the prostate volume group
of 50 to 60 g. The largest group (59%) of acute retention of
urine falls in the group with transition zone volume between
30 and 45g. On analysis of the distribution with PCAR, AUR
was present in the maximum percentage (91%) in the group
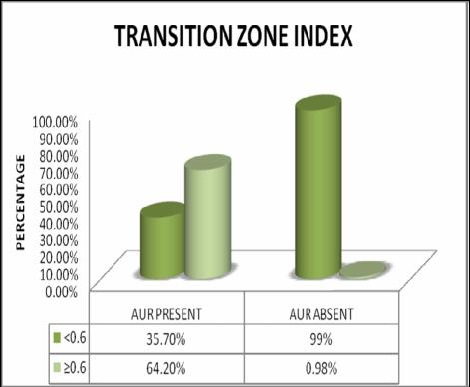
with ratio ≥0.8.In this study the TZI of ≥0.6 consists of the
maximum patients falling under the Acute Urinary Retention
group. CONCLUSION: In this study it was found that age
of the patient had a good association with the occurrence of
AUR. The association between, total prostate volume,
transition zone volume, transition zone index, PCAR and AUR
was found to be statistically significant. Duration of symptoms
was not significantly associated with the occurrence of AUR.
As the values of TZI and PCAR increased, the association
with acute retention of urine was inferred to be more
significant, there by suggesting that these indices can be used
as strong predictors of AUR. Larger studies are warranted to
detect if these parameters can be useful in deciding the mode
of management.
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, et al. The development
of human prostatic hyperplasia with age. J
Urol.1984;132:474–479.
Lepor H, Machi GM. Comparison of AUA symptom
index in unselected males and females between 55 and
years of age. Urology. 1993;42:36.
Kaplan SA, Te AE, Pressler LB, Olsson CA. Transition
zone index as a method of assessing benign prostatic
hyperplasia: correlation with symptoms, urine flow and
detrusor pressure. J Urol 1995;154:1764-9.
Lepor H, Nieder A, Feser J, O’Connell C, Dixon C. Total
prostate and transition zone volumes, and transition zone
index are poorly correlated with objective measures of
clinical benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 1997;158:85-8.
Kurita Y, Masuda H, Terada H, Suzuki K, Fujita K.
Transition zone index as a risk factor for acute urinary
retention in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology
;51:595-600.
Jin Liang et al – Implications of prostatic volume
measurements on the degree of bladder outlet obstruction
in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia and LUTS. JTUA
Vol. 17 no 2, june 2006
Darius et al – Importance of prostate volume and
urinary flow rate in prediction of BOO in men with
symptomatic BPH. – CEJU 2011/64/2
DAimantus et al – PSA and TZI – Powerful predictors of
AUR in men with BPH (medicina (2003) vol 39, no 11
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities