A Case of Fundus Falvimaculatus (A Phenotypic Variant of Stargardt Disease)
Abstract
A 13 years old male attended OPD with chief complaints of progressive painless diminution of vision - 2 years. There was h/o perception of wavy lines and defective dark adaptation. There was no h/o defective field of vision or any history suggestive of cranial nerve dysfunction.
General and systemic examinations were normal. The vision was 6/24 OU. Anterior segment examination was normal OU. Colour vision was defective in both the eyes. Dilated fundus examination showed OU - Beaten bronze appearance of Macula with pisciform flecks distributed throughout the fundus with absent foveal reflex.
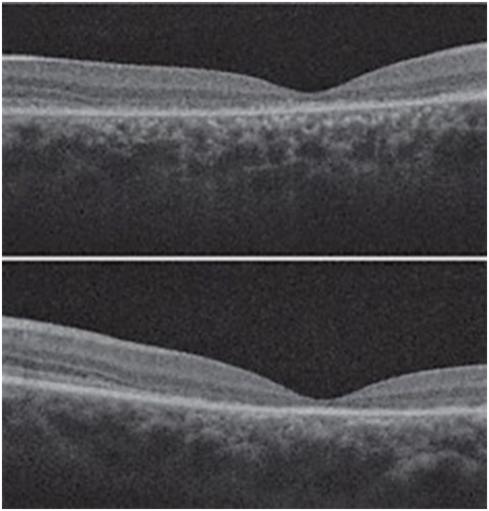
Further investigations like FFA, EOG and OCT were done. OU fundus fluorescein angiography showed fundus autofluorescence and silent choroid. Electroretinogram was normal. OCT showed reduced foveal thickness in both eyes.
Owing to the presence of progressive painless loss of vision, beaten bronze appearance of macula with diffuse pisciform flecks, fundus auto fluorescence, with FFA showing dark and silent choroid, the patient was diagnosed to have Fundus flavimaculatus, a phenotypic form of Stargardts disease and was prescribed low vision aids. Reassurance was given.
This case is presented for its visual manifestations and characteristic fundus findings.
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Franceschetti, A & François, J. Fundus Flavimaculatus Arch. Ophthalmol. 25, 505–530 (1965).
Hadden, O.B. & Gass, J.D. Fundus flavimaculatus and Stargardt's disease. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 82,527–539 (1976).
Merin, S. Inherited macular diseases. in Inherited eye diseases (Marcel Dekker) 137–175 (1991).
Fishman, G.A. Fundus flavimaculatus. A clinical classification. Arch. Ophthalmol. 94, 2061–2067 (1976).
Gass, J.D.M. in: Stereoscopic Atlas of Macular Diseases. C. V. Mosby, St. Louis; 1970:122.
Newell, F.W., Krill, A.E., Farkas, T.G. Drusen and fundus flavimaculatus. Clinical, functional, and histologic haracteristics. Trans. Am. Acad. Ophthalmol. Otolaryngol. 1972;76:88.
Ernest, J.R., Krill, A.E. Fluorescein studies in fundus flavimaculatus and drusen. Am. J. Ophthalmol.1966;62:1.
Irvine, A.R., Wergeland, F.L. Jr. Stargardt's hereditary progressive macular degeneration. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1972; 56: 817.
Krill, A.E., Klein, B.A. Flecked retina syndrome. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1965;74:496.
Fish, G., Grey, R., Sehmi, K.S. & Bird, A.C. The dark choroid in posterior retinal dystrophies. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 65, 359–363 (1981).
Rupps,H. et al. Progressive cone dystrophy. Ophthalmology
,1401–1409 1987).
Deutman, A. Macular dystrophies. in Genetic and Metabolic Eye Disease (eds Morton F. & Goldberg M.D, 367–429, 1974).
Klein, B.A., Krill, A.E. Fundus flavimaculatus: Clinical, functional, and histopathologic observations.Am.J. Ophthalmol. 1967;64:3.
Eagle, R.C., Lucier, A.C., Bernardino, V.B. & Yanoff, M. Retinal pigment epithelial abnormalities in fundus flavimaculatus. Ophthalmology 87, 1189–1200 (1980).
Lathrop, G.M., Lalouel, J.M., Julier, C. & Ott, J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am. J. hum. Genet. 37, 482–498 (1985).
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities